⚠️ CRITICAL SECURITY COMPONENT – Handle with extreme care!
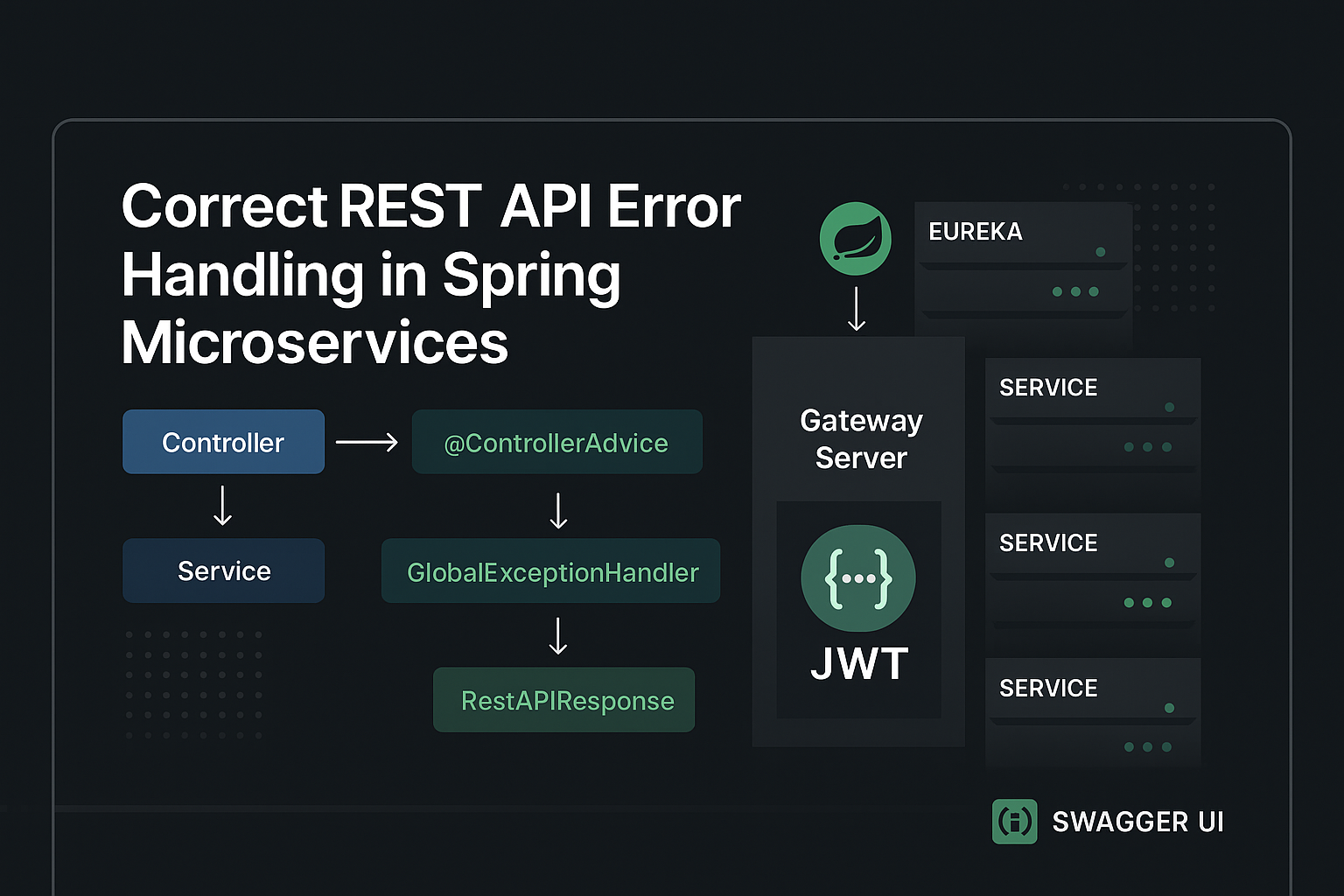
Architecture Overview
AdventureTube uses hybrid authentication:
- Google OAuth → User signs in with Google
- Google ID Token → Sent to AdventureTube backend
- JWT Tokens → Backend returns access + refresh tokens
- API Authorization → JWT access token used for all API calls
Token Storage
UserModel Structure
struct UserModel: Codable {
// AdventureTube JWT Tokens
var adventuretubeJWTToken: String? // Access token
var adventuretubeRefreshJWTToken: String? // Refresh token
// Google Authentication
var idToken: String?
var googleUserId: String?
// User Identity
var adventureTube_id: UUID?
}| Token | Purpose | Lifetime | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
adventuretubeJWTToken |
API authorization | Short-lived | UserDefaults |
adventuretubeRefreshJWTToken |
Token renewal | Long-lived | UserDefaults |
idToken |
Google authentication | Session | UserDefaults |
Authentication Endpoints
A. User Registration
POST /auth/users – Register new user with Google ID token
B. Login (Token Exchange)
POST /auth/token – Exchange Google ID token for JWT tokens
C. Token Refresh
POST /auth/refreshToken – Get new token pair when access token expires
D. Logout
POST /auth/logout – Invalidate refresh token on server
Error Handling
| Code | Meaning | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| 401 | Unauthorized | Refresh OAuth token |
| 404 | Not Found | User doesn’t exist |
| 409 | Conflict | Duplicate registration |
| 500 | Server Error | Retry with backoff |
Security Best Practices
✅ Use LoginManager.shared.userData for tokens
✅ Clear tokens on sign out via loginState = .signedOut
✅ Test token refresh flow thoroughly
✅ Handle auth errors gracefully in UI
❌ NEVER log tokens in production code
❌ NEVER store tokens in separate locations
❌ NEVER hardcode tokens or credentials